Accumulators can be divided into spring type, heavy hammer type and gas type according to the loading mode.
The spring accumulator relies on the compression spring to convert the excess pressure energy in the hydraulic system into spring potential energy for storage and release when necessary. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure and low cost. However, because the expansion and contraction energy of the spring is limited, and the expansion and contraction of the spring is not sensitive to pressure changes, and the vibration elimination function is poor, it is only suitable for small capacity, low pressure systems (P ≤ 1.0~1.2MPa), or as a buffer device.
The heavy hammer accumulator converts the pressure energy in the hydraulic system into gravitational potential energy and stores it by lifting the mass loaded on the sealing piston. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure and stable pressure. The disadvantage is that the installation is limited and can only be installed vertically; Not easy to seal; The mass block has large inertia and is insensitive. This type of accumulator is only used for temporary energy storage. These two types of accumulators are rarely used because of their limitations. However, it is worth noting that some research departments have made some improvements in the structure of these two types of accumulators from an economic perspective, which has overcome their shortcomings to a certain extent. For example, a domestic factory adopts the method of improving the structure of the spring accumulator, increasing the outer diameter of the spring and limiting the spring stroke, which improves the working pressure and capacity of the accumulator and reduces the cost.
The working principle of the gas accumulator is based on Boyle's law. The energy is converted by compressing the gas. When using, the accumulator is first charged with gas of predetermined pressure. When the system pressure exceeds the internal pressure of the accumulator, the oil compresses the gas and converts the pressure in the oil into the internal energy of the gas; When the system pressure is lower than the internal pressure of the accumulator, the high-pressure gas of the oil in the accumulator flows to the external system to release energy. The key to this kind of accumulator is to select an appropriate charging pressure. This type of accumulator can be divided into pipeline vibration absorber, gas-liquid direct contact type, piston type, diaphragm type, air bag type, etc. according to the structure.
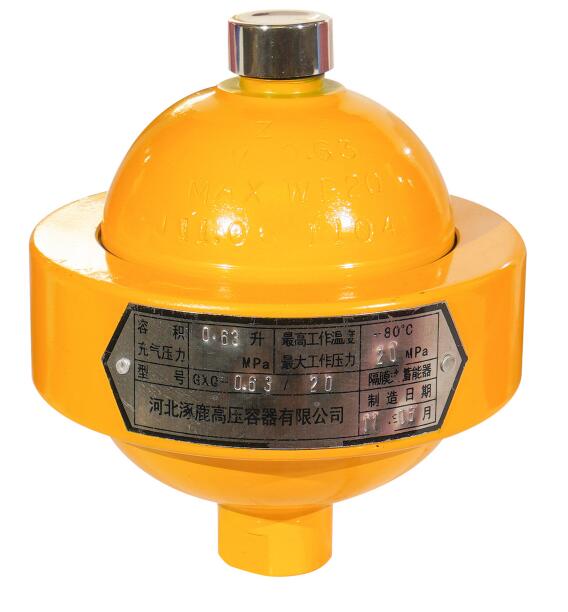
The bladder type accumulator (as shown in Figure 1-3) is composed of forged or cast pressure tank, bladder, gas inlet valve and oil inlet valve. The material of the leather bag is according to the standard, usually using nitrile rubber, butyl rubber, fluorinated rubber, ethylene oxide epoxy chloropropane rubber and other materials.
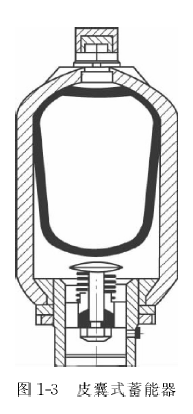
The bladder accumulator is composed of a pressure resistant shell, an elastic airbag, an inflation valve, a poppet valve, an oil port, etc. The accumulator can be made into various specifications and is suitable for various hydraulic systems; The capsule has small inertia and sensitive response, and is suitable for eliminating pulsation; It is not easy to leak gas, and there is no possibility of oil and gas mixing; It is easy to maintain, less accessory equipment, easy to install, and convenient to inflate. It is currently the most used.
The pipeline vibration absorber is a short tubular accumulator directly installed on the high-pressure system management. This accumulator has good response performance and can well eliminate the high-frequency oscillation in the high-pressure frequency system. It is mostly used in the high-pressure vibration elimination system.
The gas-liquid direct contact accumulator is charged with inert gas. The advantages are large capacity, sensitive response, small inertia of moving parts, and no mechanical wear. However, due to the direct contact between gas and liquid, the size is small and the inflation pressure is limited; It is difficult to seal, and the possibility of gas-liquid mixing is high. Therefore, the gas consumption of the accumulator is large, the components are prone to cavitation, and the volume utilization rate is low. There are many auxiliary equipment and large investment.
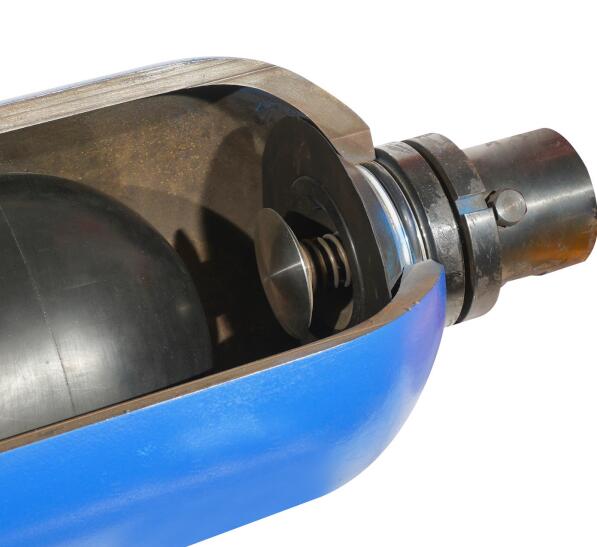

The piston accumulator uses the piston to separate gas and liquid. There is a seal between the piston and the inner wall of the cylindrical accumulator, so the oil is not easy to be oxidized. The accumulator has long service life, light weight, easy installation, simple structure, convenient maintenance, but poor reaction sensitivity, and is not suitable for low pressure pulse absorption.
Diaphragm accumulators are two hemispherical shells buckled together, and a rubber diaphragm is clamped between the two hemispheres to separate oil and gas. Its weight to volume ratio is minimum, its response is sensitive, and its pulsation elimination effect under low pressure is remarkable. The rubber film area of diaphragm accumulator is small, and the gas expansion is limited, so the inflation pressure is limited and the capacity is small.
