The vehicle hydrostatic energy storage transmission system is shown in the figure.
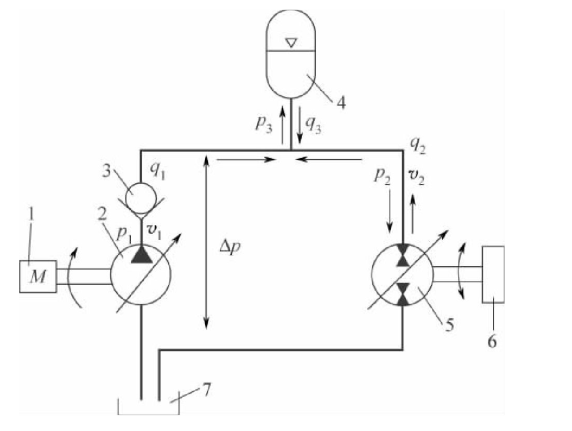
In this system, because of the existence of the accumulator, there is no direct connection between the flow of the hydraulic pump q1 and the variable displacement motor q2 in the system. The flow difference (q3=q1-q2) will directly flow into or out of the hydraulic accumulator, that is, the hydraulic pump and the variable displacement motor have independent rotational speeds. The variable displacement motor adopts a symmetrical structure. Through the axial piston swashplate structure at the zero point, the variable displacement motor can work completely reversibly, that is, the size and direction of the displacement V2 can be changed. Variable motor can work in four quadrants. When variable motor works in one quadrant, it drives the vehicle forward; Drive the vehicle backward during the three image limit, that is, the reverse gear condition of the vehicle is achieved by changing the rotation direction of the variable displacement motor; When the two quadrants and four quadrants are respectively forward and backward braking conditions. The hydrostatic transmission system adapts to the change of external load and the change of motor working condition by adjusting the tilt angle and direction of the swashplate of the variable displacement motor.
After adding the energy storage element accumulator to the vehicle transmission system, the working mode of the transmission system has changed greatly. It is mainly shown in:
① When the vehicle starts, the engine or accumulator or both provide energy to drive the vehicle;
② Only the engine provides energy to drive the vehicle to start and drive, and at the same time, the accumulator is filled with liquid. When the system reaches the specified pressure, the engine shuts down or is at idle speed. At this time, the accumulator provides the energy required for vehicle driving. Until the requirements for vehicle driving cannot be met, the engine starts to work normally again and remains near the corresponding economic working area. When peak power is required, the accumulator will supplement it; ③ When the vehicle decelerates or brakes, the engine stops or idles, and the hydraulic motor operates in the mode of pump working condition. The inertia energy of the vehicle is converted into hydraulic energy and stored in the accumulator, which is released as needed to drive the vehicle, so that the brake energy can be recovered (usually dissipated in the form of heat energy in the brake).
Therefore, the main characteristics of the vehicle hydrostatic energy storage transmission system are:
① The engine can work intermittently to reduce fuel consumption and emissions;
② The secondary regulation technology is adopted to completely separate the engine load from the working load;
③ The accumulator can provide fractional power and reduce the installed capacity of the engine;
④ It can reduce braking frequency and realize partial braking energy recovery;
⑤ It is easy to realize vehicle direct drive/all wheel drive, and the test vehicle structure is relatively simple, reducing the vibration and noise caused by mechanical transmission;
⑥ Improve the vehicle's maneuverability, driving stability and riding comfort.