There are several ways to check the charging pressure of the accumulator.
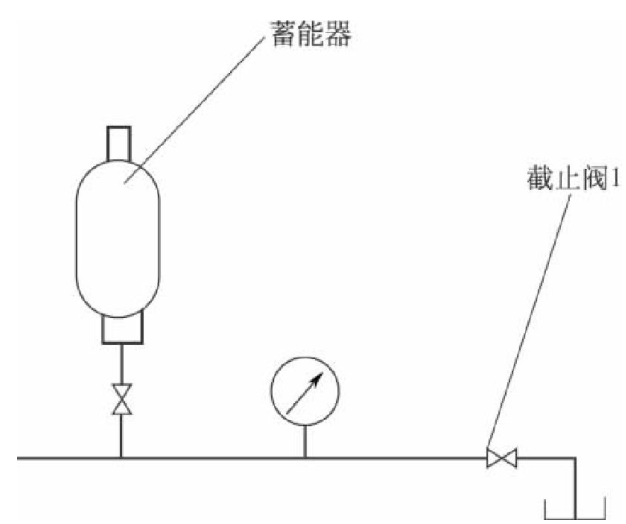
①During detection, connect the pressure detection circuit of the accumulator as shown in the figure, set a stop valve 1 between the oil inlet of the accumulator and the oil tank, and install a pressure gauge in front of the stop valve 1. Slowly open the stop valve 1 to allow the pressure oil to flow back to the oil tank. Observe the pressure gauge. The pointer of the pressure gauge drops slowly at first, reaches a certain pressure value and then drops to 0, and the reading when the pointer movement speed changes (that is, a certain pressure value when the value of the pressure gauge drops to 0), It is the inflation pressure.
②Use the inflation tool to directly check the inflation pressure, but each time the inspection will release some gas, so this method should not be used for the accumulator with small capacity. Someone connected the pressure gauge to the charging port of the accumulator to check the charging pressure. Frequent sharp pressure rise and drop and pressure fluctuation during the system operation will cause the pressure gauge pointer to swing violently, which is inappropriate.
③Check the inflation pressure with the aid of oil drain; Use the stop valve on the oil circuit between the oil inlet of the accumulator and the oil tank, as well as the pressure gauge in front of the stop valve, or use each measuring nozzle in the oil circuit to connect the stop valve and pressure gauge. During monitoring, slowly open the stop valve to allow the pressure to flow back to the oil tank. The pointer of the pressure gauge slowly drops to 0 after reaching a certain pressure value. The reading of the pressure gauge at this position is the charging pressure of the accumulator.
④In the same way, use the stop valve and pressure gauge in ③. First open the stop valve, let the system pressure drop to 0. Close the stop valve, and start the pump. The system pressure will suddenly rise to a certain value and then rise slowly. The reading of the pressure gauge at this position is the charging pressure of the accumulator.
The above two methods are simple and do not require too many copying devices. However, the measurement of the charging pressure of the smaller capacity accumulator or the influence of the actuator in the system is often difficult to detect, and is greatly affected by the human factors of the measurer, which can only be used as a rough judgment.
⑤On some units, a pressure sensor is installed on the charging valve of the more important accumulator to monitor the charging pressure of the accumulator in real time.
In addition to regularly checking the charging pressure of the accumulator, the charging pressure of the accumulator should be checked if the following phenomena are found during operation and maintenance.
①When the actuator does not act, the hydraulic pump acts frequently.
②The hydraulic pump is automatically started once for each action of the small stroke actuator, and each start time is very short.
③When testing the start and stop pressure of the pump, the difference between the start pressure and the stop pressure of the pump is very large, far exceeding the specified value, and the pressure rises rapidly during the operation of the pump.
④The response speed of the actuator becomes slow.
The accumulator with insufficient or zero pressure shall be refilled to the specified pressure. For the accumulator that cannot be charged or the gas overflows from the hydraulic system oil tank during charging, its leather bag or diaphragm has been damaged. The bladder accumulator can be used after replacing the leather bag. The diaphragm accumulator can only be replaced with a new one, and the service life of the diaphragm accumulator is short.
